[논문리뷰] DiffWave: A Versatile Diffusion Model for Audio Synthesis
ICLR 2021. [Paper] [Page]
Zhifeng Kong, Wei Ping, Jiaji Huang, Kexin Zhao, Bryan Catanzaro
Computer Science and Engineering, UCSD | NVIDIA | Baidu Research
30 Mar 2021
Introduction
대부분의 이전 waveform 모델은 유익한 local conditioner (ex. mel-spectrogram, 언어 feature)를 사용하여 오디오 합성에 중점을 두지만 unconditional한 생성에 대한 몇 가지 예외만 있다. Autoregressive model (ex. WaveNet)은 unconditional 설정에서 만들어진 단어와 같은 사운드 또는 좋지 못한 샘플을 생성하는 경향이 있는 것으로 나타났다. 조건 정보 없이 매우 긴 시퀀스(ex. 1초 음성에 대해 16,000개의 timestep)를 생성해야 하기 때문이다.
Diffusion model은 Markov chain을 사용하여 간단한 분포(ex. 가우시안 분포)를 점차 복잡한 데이터 분포로 변환하는 유망한 생성 모델 클래스다. 데이터 likelihood는 다루기 어렵지만 ELBO를 최적화하여 diffusion model을 효율적으로 학습할 수 있다. 가장 최근에는 denoising score matching과 연결된 이미지 합성에서 특정 parameterization이 성공적으로 나타났다. Diffusion model은 학습 가능한 파라미터 없이 diffusion process를 사용하여 학습 데이터에서 latent를 얻을 수 있다. 따라서 다른 모델(ex. VAE의 인코더 또는 GAN의 discriminator)과 달리 학습에 추가 신경망이 필요하지 않다. 이렇게 하면 두 네트워크의 공동 학습에서 발생하는 까다로운 “posterior collapse” 또는 “mode collapse” 문제를 피할 수 있으므로 고충실도 오디오 합성에 유용하다.
본 논문에서는 오디오 합성을 위한 다목적 diffusion model인 DiffWave를 제안하였다. DiffWave는 이전 연구들에 비해 몇 가지 장점이 있다.
- Autoregressive가 아니므로 고차원 waveform을 병렬로 합성할 수 있다.
- Latent와 데이터 사이에 전단사(bijection)를 유지해야 하는 flow 기반 모델과 달리 아키텍처 제약을 부과하지 않기 때문에 유연하다.
- 고충실도 합성을 위해 보조 loss (ex. 스펙트로그램 기반 loss) 없이 단일 ELBO 기반 목적 함수를 사용한다.
- Conditional 및 unconditional waveform 생성 모두에 대해 고품질 오디오 신호를 생성하는 다목적 모델이다.
Diffusion Probabilistic Models
(자세한 내용은 DDPM 논문리뷰 참고)
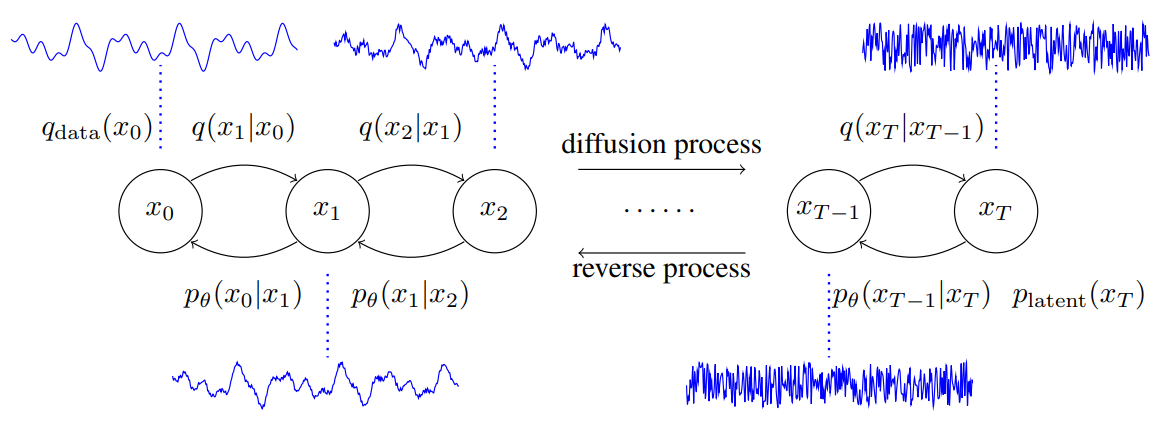
Diffusion process:
\[\begin{equation} q(x_1, \cdots, x_T \vert x_0) = \prod_{t=1}^T q(x_t \vert x_{t-1}) \\ q(x_t \vert x_{t-1}) = \mathcal{N} (x_t; \sqrt{1 - \beta_t} x_{t-1}, \beta_t I) \end{equation}\]Reverse process:
\[\begin{equation} p_\textrm{latent} (x_T) = \mathcal{N} (0, I) \\ p_\theta (x_0, \cdots, x_{T-1} \vert x_T) = \prod_{t=1}^T p_\theta (x_{t-1} \vert x_t) \end{equation}\]Parameterization:
\[\begin{equation} \mu_\theta (x_t, t) = \frac{1}{\alpha_t} \bigg( x_t - \frac{\beta_t}{\sqrt{1 - \bar{\alpha}_t}} \epsilon_\theta (x_t, t) \bigg) \\ \sigma_\theta (x_t, t) = \tilde{\beta}_t^{\frac{1}{2}} \\ \textrm{where} \quad \alpha_t = 1 - \beta_t, \quad \bar{\alpha}_t = \prod_{s=1}^t \alpha_s, \quad \tilde{\beta}_t = \frac{1 - \bar{\alpha}_{t-1}}{1 - \bar{\alpha}_t} \beta_t \end{equation}\]목적 함수:
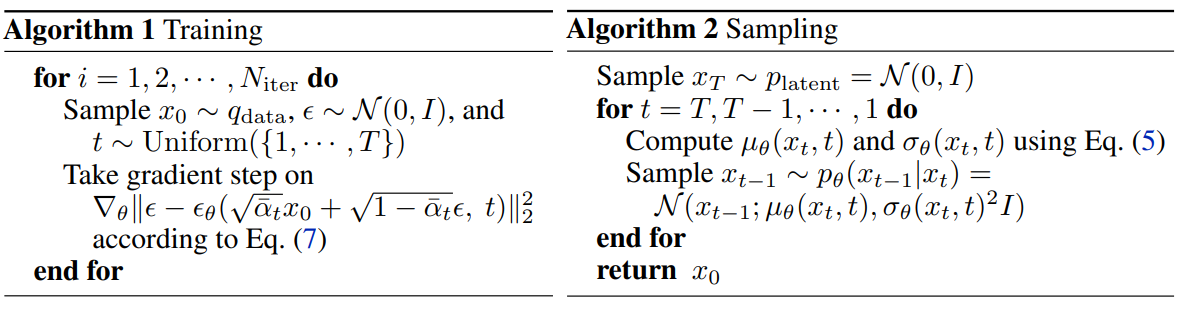
\[\begin{equation} \min_\theta L_\textrm{unweighted} (\theta) = \mathbb{E}_{x_0, \epsilon, t} \| \epsilon - \epsilon_\theta (\sqrt{\vphantom{1} \bar{\alpha}_t} x_0 + \sqrt{1 - \bar{\alpha}_t} \epsilon, t) \|_2^2 \end{equation}\]Algorithm:
Diffwave Architecture
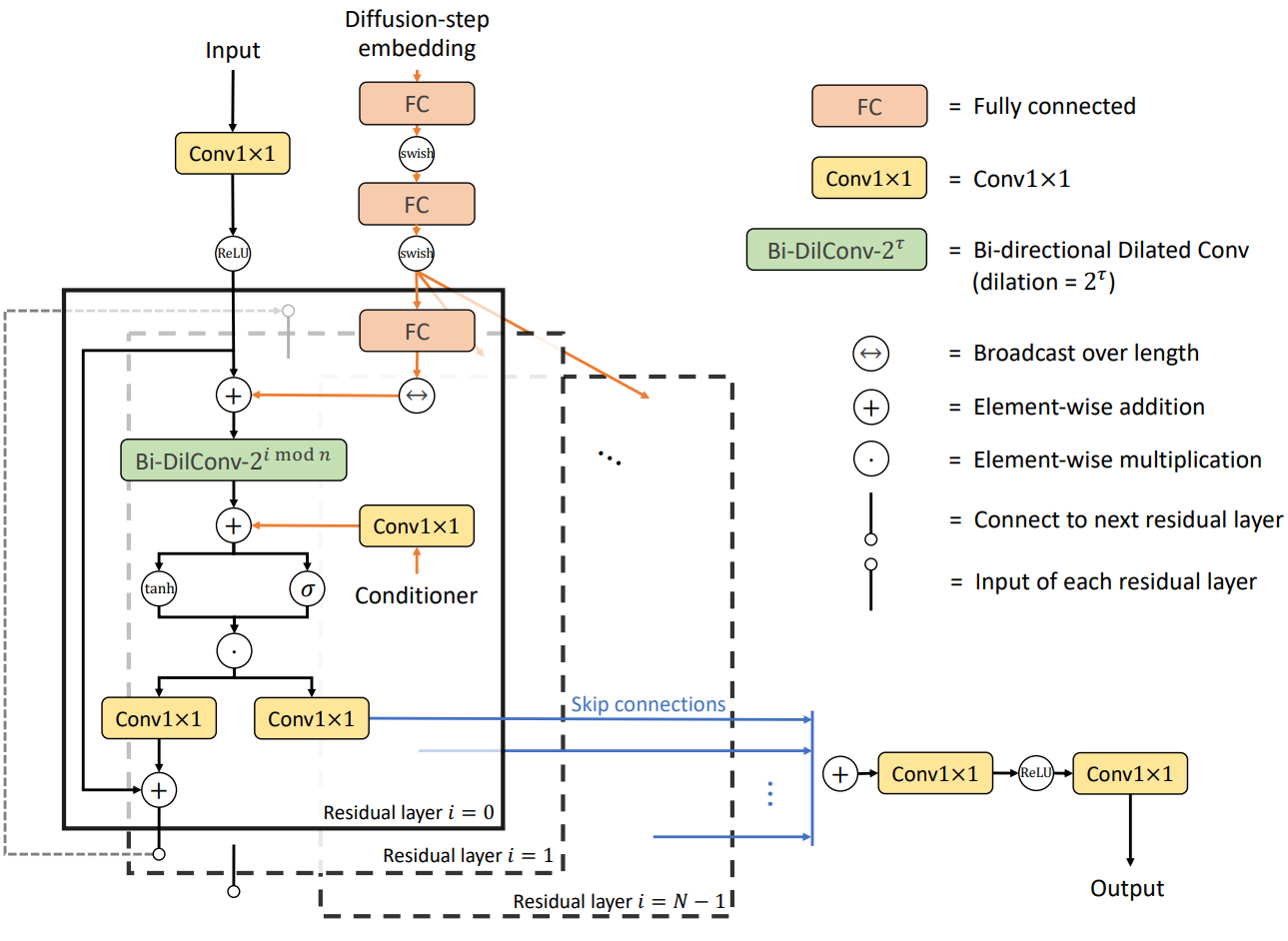
WaveNet과 다른 bidirectional dilated convolution (Bi-DilConv) 아키텍처를 기반으로 네트워크 $\epsilon_\theta : \mathbb{R}^L \times \mathbb{N} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^L$을 구축한다. 네트워크는 autoregressive가 아니므로 latent $x_T$에서 길이가 $L$인 오디오 $x_0$을 생성하려면 $T$ step의 forward pass가 필요하다. 여기서 $T$는 waveform 길이 $L$보다 훨씬 작다. 네트워크는 $C$개의 residual channel이 있는 $N$개의 스택으로 구성된다. 이러한 레이어는 $m$개의 블록으로 그룹화되고 각 블록은 $n = N / m$개의 레이어를 가진다. 각 레이어에서 kernel size가 3인 Bi-DilConv을 사용한다. Dilation은 각 블록 내의 각 레이어에서 두 배가 된다. WaveNet에서와 같이 모든 residual layer의 skip connection을 합산한다.
1. Diffusion-step Embedding
모델이 여러 $t$에 대해 다른 $\epsilon_\theta (\cdot, t)$를 출력해야 하므로 입력의 일부로 diffusion step $t$를 포함하는 것이 중요하다. 각 $t$에 대해 128차원 인코딩 벡터를 사용한다.
\[\begin{equation} t_\textrm{embedding} = [ \sin (10^{\frac{0 \times 4}{63}} t), \cdots, \sin (10^{\frac{63 \times 4}{63}} t), \cos (10^{\frac{0 \times 4}{63}} t), \cdots, \cos (10^{\frac{63 \times 4}{63}} t) ] \end{equation}\]그런 다음 인코딩에 3개의 fully connected (FC) layer를 적용한다. 여기서 처음 두 FC는 모든 residual layer 간에 파라미터를 공유한다. 마지막 residual layer별 FC는 두 번째 FC의 출력을 $C$차원 임베딩 벡터로 매핑한다. 그 다음 길이에 따라 이 임베딩 벡터를 브로드캐스트하고 모든 residual layer의 입력에 추가한다.
2. Conditional Generation
Local conditioner
본 논문에서는 DiffWave를 mel spectrogram을 조건으로 하는 vocoder로 테스트한다. 먼저 transposed 2D convolutions을 통해 mel spectrogram을 waveform과 동일한 길이로 업샘플링한다. 레이어별 Conv1×1이 해당 mel-band를 $2C$개의 채널로 매핑한 후 conditioner가 각 residual layer의 dilated convolution에 대한 바이어스 항으로 추가된다.
Global conditioner
많은 생성 작업에서 조건부 정보는 글로벌한 개별 레이블(ex. speaker ID, 단어 ID)로 제공된다. 모든 실험에서 차원이 128인 공유 임베딩을 사용한다. 각 residual layer에서 128을 $2C$개의 채널에 매핑하기 위해 레이어별 Conv1×1을 적용하고 각 residual layer의 dilated convolution 후에 임베딩을 바이어스 항으로 추가한다.
3. Unconditional Generation
Unconditional 생성 task에서 모델은 조건 정보 없이 일관된 발화를 생성해야 한다. 네트워크의 출력 단위가 발화의 길이 $L$보다 큰 receptive field 크기 $r$을 갖는 것이 중요하다. 실제로, $r \ge 2L$이 필요하므로 가장 왼쪽과 가장 오른쪽 출력 unit에는 전체 $L$ 차원 입력을 포함하는 receptive field가 있다.
Dilated convolution layer 스택의 경우 출력의 receptive field 크기는 최대 $r = (k − 1) \sum_i d_i + 1$이다. 여기서 $k$는 kernel size고 $d_i$는 $i$번째 residual layer에서의 dilation이다. 예를 들어, 30개의 layer로 이루이어진 dilated convolution은 receptive field 크기 $r = 6139$를 가진다. 이는 16kHz 오디오의 0.38s에 불과하다. 레이어 수와 dilation cycle 크기를 더 늘릴 수 있다. 그러나 더 깊은 레이어와 더 큰 dilation cycle은 품질을 저하시킨다. 이는 WaveNet의 경우 특히 그렇다. DiffWave는 출력 $x_0$의 receptive field를 확대하는 데 이점이 있다. Reverse process에서 $x_T$에서 $x_0$까지 반복하면 receptive field 크기가 $T \times r$까지 증가할 수 있으므로 DiffWave는 unconditional한 생성에 적합하다.
Experiments
- Training
- NVIDIA 2080Ti GPU 8개
- Adam optimizer, Batch size 16, Learning rate: $2 \times 10^{-4}$, 100만 step
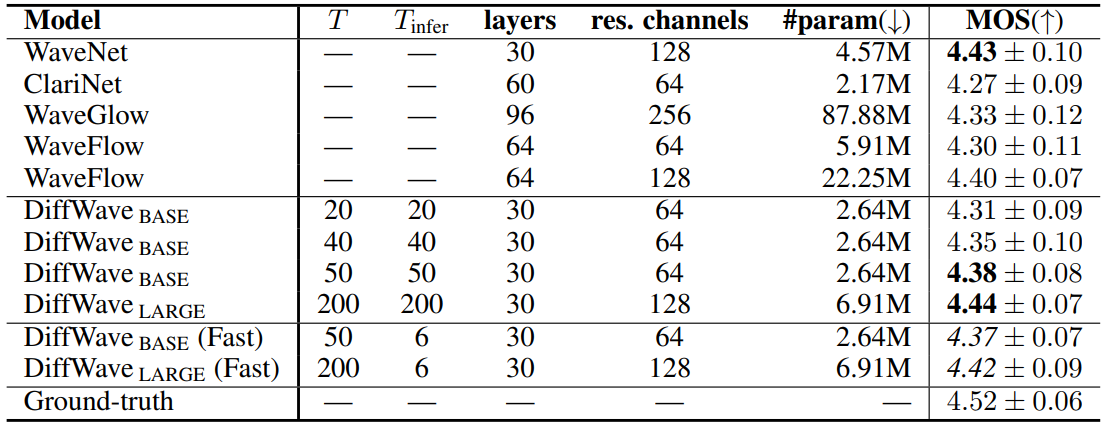
1. Neural Vocoding
- 데이터셋: LJ speech
- Conditioner: 80-band mel spectrogram
2. Unconditional Generation
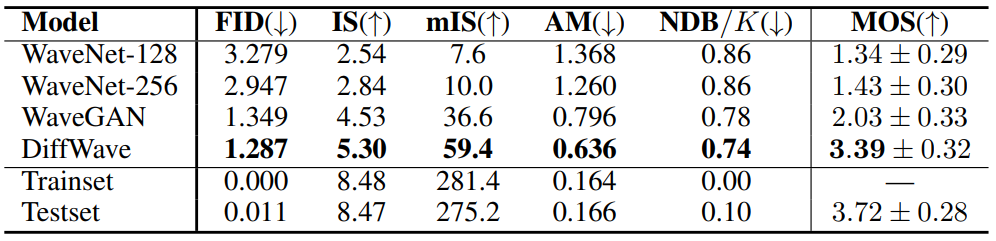
- 데이터셋: Speech Commands
- Conditioner: 80-band mel spectrogram
3. Class-Conditional Generation
Unconditional Generation의 세팅에서 레이블 conditioner만 추가